Scientists Hack CO2: Turns Pollution into Clean Fuel in 3 Shocking Steps!
CO2, a greenhouse gas, can be turned into clean fuel like methane using a process called CO2RR. Researchers are developing better catalysts and using flow cell designs to improve this process. This technology has the potential to reduce greenhouse gases and generate clean energy.
CONTENTS: Scientists Hack CO2: Turns Pollution into Clean Fuel in 3 Shocking Steps!

CO2 to methane: clean energy solution
Scientists Hack CO2: Turns Pollution into Clean Fuel in 3 Shocking Steps!
Transforming CO2 into Methane: An Innovative Solution for Clean Energy
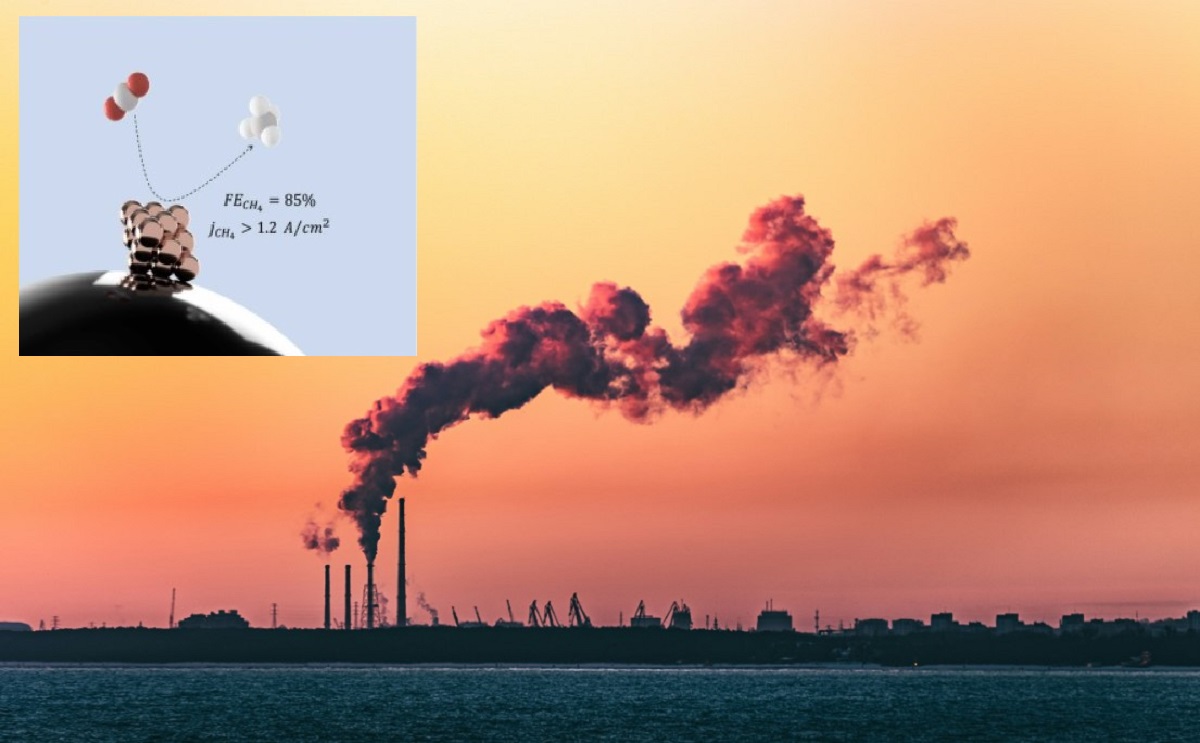
Reducing greenhouse gases such as CO2 is essential to combating global warming. One promising method is the electrochemical CO2 reduction reaction (CO2RR), which converts CO2 into useful fuels like methane using renewable electricity from sources like wind, hydro, and solar power. This process not only reduces CO2 emissions but also generates reliable energy.
New Catalysts for Efficient Methane Production
While methane is often criticized for being a potent greenhouse gas, it can serve as a clean and efficient energy source when produced and used responsibly. Methane, the primary component of natural gas, is widely used for electricity and heating. Producing methane through CO2RR provides a way to recycle CO2 into a valuable fuel, reducing reliance on fossil fuels and helping to close the carbon loop.
Researchers have developed new catalysts to improve the efficiency of converting CO2 to methane. Techniques such as using copper-supported iron-single-atom catalysts, incorporating copper ions into a cerium oxide matrix, employing less alkaline electrolytes, and doping copper with other metals like gallium have shown promising results.
Despite these advancements, challenges remain in making the process efficient and cost-effective. Currently, producing methane through these methods is more expensive than traditional methods. However, continued research and development may help overcome these hurdles, making CO2RR a viable solution for both reducing greenhouse gases and producing clean energy.
Better catalysts, cleaner methane fuel
Enhancing CO2 to Methane Conversion: Advances in Catalyst Design and Electrolyte Optimization
Traditional CO2 conversion methods face challenges with CO2 diffusion, but using a flow cell design can improve the process. In these setups, a gas diffusion electrode (GDE) separates CO2 gas from the electrolyte, facilitating the effective use of highly alkaline solutions. This approach reduces resistance and increases current density, though it can also produce unwanted byproducts like ethylene.
Importance of Catalyst Size and Shape
The size and shape of catalysts, particularly copper, are critical in optimizing methane production. Recent studies have demonstrated that smaller copper nanoparticles favor methane production over ethylene.
Researchers have experimented with copper nanoparticles ranging from 0.5 nm to 200 nm, discovering that smaller particles shift the reaction towards methane. Tests conducted in flow cell setups confirmed these findings, achieving high methane production with stable performance over time.
Boosting Efficiency Through Design Improvements
By improving catalyst design and optimizing electrolytes, scientists have significantly enhanced the efficiency of methane production from CO2. Focusing on the right size and shape of catalysts has led to methods that achieve high methane production rates.
These advancements make the electrochemical CO2 reduction reaction (CO2RR) a more promising and sustainable technology for generating methane, effectively transforming a greenhouse gas into a clean energy solution.
Check out TimesWordle.com for all the latest news